USE AdventureWorks2008 GO SELECT t.name, t1.name, t.name, t1.name, c.name, c.max_length, c.precision, c.collation_name FROM sys.TABLES t JOIN sys.COLUMNS c ON t.object_id = c.object_id JOIN sys.types t1 ON c.user_type_id = t1.user_type_id WHERE t.name = 'Employee'
Monday, September 30, 2013
List All columns of a Table with their data type
How to check the installed version of powershell
The Easy Way, in the powershell prompt type:
PS D:\> $host.Version
Major Minor Build Revision
----- ----- ----- ------
2 0 -1 -1
Monday, September 2, 2013
Wednesday, August 21, 2013
system_health session incidentally dropped
The session can be recreated using the file u_tables.sql (the script is at the bottom of the file) that is located in :
C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL10.SQL2008\MSSQL\Install\
Wednesday, August 14, 2013
Wednesday, August 7, 2013
List disabled Jobs and their schedule
To List the disabled Jobs and their relative schedules , you can run the following query:
USE msdb GO SELECT ss.schedule_id , J.name, ss.name, J.enabled [Job Enabled ?], ss.enabled [Schedule ENABLED ?] FROM sysjobs J JOIN sysjobschedules s ON J.job_id = s.job_id JOIN sysschedules ss ON s.schedule_id = ss.schedule_id WHERE J.enabled = 0
Thursday, July 11, 2013
List all tables with their schema name in a database
SELECT T.name ,S.name FROM sys.tables T JOIN sys.schemas S ON T.schema_id = S.schema_id ORDER BY T.name ASC
Monday, April 29, 2013
Compact and Repair in Microsoft Access 2007
1. Click on the Office Button
2. Choose Manage then Compact and Repair Database
3. on the task bar you can see the progress bar showing that the database is compacting:
Monday, April 8, 2013
Control the zoom of pdf files
I read a lot of pdf files. One thing I always found rather annoying is that the pdf files open at very high zoom percentage , something like 263% so I have to adjust the zoom for every document.
Fixing this is easy, Go to Edit | Preferences :
Then Go to Page Display | Default Layout and Zoom :
Choose the desired value. That’s it , the next time you’ll open pdf documents, the zoom will be 100%.
Friday, March 29, 2013
Search Arguments : impact on query plans
For those who may be starting out with query execution plans, it may be interesting to consider the use of Search arguments (SARG) in queries. The use of SARG has 2 objectives :The first query uses and index scan with the following cost :
If the filter is not a SARG then typically an index scan or table scan is performed on the entire table or index.
- Limit the number of rows returned by the query
- Use an index seek operation to improve the performance of the query
2 points to remember :
A simple Example using AdventureWorks2008:
- A filter expression is not a SARG if the column is used in an expression such as YEAR(OrderDate) or LEFT(Employee.Name,1)=’B’
- The use of the COLLATE operator on a column invalidates the use of and index on that column.
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX OrderDateIndex ON Sales.SalesOrderHeader ( Orderdate )
GO
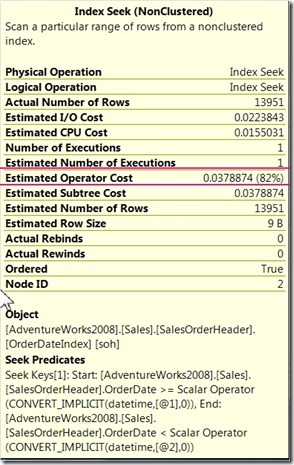
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Sales.SalesOrderHeader sohThese 2 queries will generate the following Query plans:
WHERE YEAR(soh.OrderDate )
=2004
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Sales.SalesOrderHeader soh
WHERE soh.OrderDate >= '20040101' AND soh.OrderDate < '20050101'

as you can see the second query plan cost is reduced by using a SARG in the query resulting in the use of the index seek operator, that allows SQL server to use a balanced tree to search the records.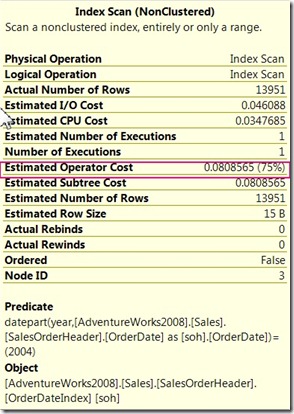
Thursday, March 28, 2013
Join tip – Inner Joins when using ON and WHERE Clause
When tuning queries, one the first basic strategies is to minimize the use of joins. Additionally outer joins incur more cost than inner joins as they require extra work to retrieve unmatched rows.
TIP : If only inner joins are used , the ON and WHERE Clause behave the same. Consider the following queries:
you can see that the execution plans generated for both queries are the same:
If the queries would have been written with outer join, they would have different query plans.
Monday, March 11, 2013
List All plans in the cache SQL Server 2008
SELECT [cp].[refcounts] , [cp].[usecounts] , [cp].[objtype] , [st].[dbid] , [st].[objectid] , [st].[text] , [qp].[query_plan] FROM sys.dm_exec_cached_plans cp CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_sql_text ( cp.plan_handle ) st CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_query_plan ( cp.plan_handle ) qp ;
Full-Text Thesaurus Files overview
These files let you define synonyms for full text queries. There is one file for every language supported by fulltext search. To list them run the following Query:
1. List Full-text languages and their LCIDs:
SELECT * FROM sys.fulltext_languages ORDER BY lcid
2. Thesaurus File location : $SQL_Server_Install_Path\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL10.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\FTData.
3. Basic File Structure
- The first element in red <diacritic_sensitive> determines if the thesaurus file is accent-sensitive or note (defaults to 0).
- <expansion> : determines a set of terms that can be substituted. A full-text query can return results using any of the three terms “Internet Explorer” or “IE” or “IE5”.
- <replacement> : one term is substituted for another, the terms in the <pad> elements are replaced by the term in the <sub> element, here “NT5” and “W2K” are replaced by “Windows 2000”, i.e if a full-text query includes either “NT5” or “W2K” the results include only content that contains “Windows 2000”.
in SQL server 2008 , you need to run sys.sp_fulltext_load_thesaurus_file as shown below :
EXEC sys.sp_fulltext_load_thesaurus_file 1033 (see above in this to find the LCID for the language).








